SWOT Analysis of Apple: Innovation, Ecosystem & Global Strategy
Explore the complete SWOT analysis of Apple in 2025. Discover how the tech giant maintains global dominance through innovation, premium branding, and ecosystem lock-in—while facing competition, regulation, and market saturation.
When we talk about innovation, premium design, and seamless user experience, Apple Inc. stands at the very top. From revolutionizing personal computing in the 1980s to reinventing smartphones with the iPhone, Apple has continuously shaped how the world interacts with technology.
In 2025, Apple is more than a hardware company—it’s a tech ecosystem that connects millions through iOS, Mac, Apple Watch, AirPods, and now, the Vision Pro. With new investments in AI, spatial computing, and services, Apple is poised to lead the next era of digital lifestyle.
But with rising global competition, regulatory crackdowns, and saturation in core markets, Apple must navigate change carefully.
In this SWOT analysis, we’ll explore Apple’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats—to understand how the world’s most valuable company plans to stay relevant, resilient, and revolutionary in 2025.
Learn AI & Digital Marketing,
Pay Fees After Placement
- ✅ Minimal Admission Fees
- ✅ No Loan or Income Sharing Agreement
- ✅ 100% Placement Support
- ✅ ISO & Govt Registered Certificate
- ✅ Practical 3+1 Months Duration
Get a free counseling call. We’ll guide you through learning, certification, and job placement.
Request a Free Call Back
Takes less than a minute.
Company Overview of Apple
Apple Inc., founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, has evolved into one of the world’s most valuable and influential technology companies. Headquartered in Cupertino, California, Apple is best known for combining elegant hardware with intuitive software to deliver seamless, high-end user experiences.
Apple at a Glance (2025):
- CEO: Tim Cook
- FY24–25 Revenue: $395+ billion
- Market Cap: ~$3 trillion
- Employees: 160,000+ globally
- Key Markets: North America, China, Europe, India
Flagship Products & Services:
- Hardware: iPhone, Mac, iPad, Apple Watch, AirPods, Vision Pro
- Software: iOS, macOS, iPadOS, WatchOS
- Services: App Store, Apple Music, iCloud, Apple TV+, Apple Fitness+, Apple Pay
- New Verticals: Spatial computing (Vision Pro), Health tech, Generative AI
Apple’s strength lies not just in its product innovation, but in building a closed-loop ecosystem where hardware, software, and services all work together—creating high retention, premium pricing, and brand loyalty worldwide.
What is a SWOT Analysis?
A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool used to evaluate a company’s internal and external positioning based on four key dimensions:
- Strengths – Internal capabilities that give a company a competitive advantage
- Weaknesses – Internal limitations that may hinder growth or agility
- Opportunities – External trends and emerging markets the company can leverage
- Threats – External risks that could impact market position or profitability
For a company like Apple, with a vast product ecosystem and global operations, a SWOT analysis is essential to understand:
- How it maintains brand dominance and innovation leadership
- Where it might be vulnerable in terms of competition, regulation, or product dependency
- What new frontiers (like AI, spatial computing, or healthcare) can define its next wave of growth
This framework gives a complete picture of how Apple stands today—and where it’s headed next.
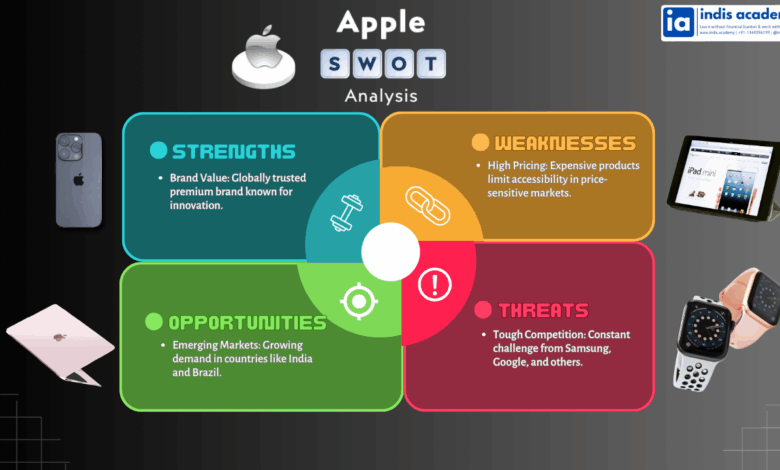
Strengths of Apple
Apple’s ability to blend cutting-edge innovation with premium brand positioning has made it one of the most influential companies on the planet. In 2025, its greatest strengths continue to come from its ecosystem, design, user experience, and loyal customer base.
Let’s explore what powers Apple’s market leadership:
1. Strong Brand Loyalty and Global Recognition
Apple has built a loyal customer base across the globe—often described as a cult following. Its consistent focus on quality, minimalism, privacy, and sleek design gives it exceptional brand equity and repeat buyers.
2. Seamless Ecosystem Integration
From iPhones and MacBooks to AirPods, Watch, and now Vision Pro, Apple’s products work better together. This “walled garden” ensures:
- Smooth continuity across devices
- Data sync via iCloud
- Higher switching costs for users
3. Product Innovation and In-House Chip Design
Apple’s transition to M-series chips (Mac) and A-series processors (iPhone) gives it unmatched control over:
- Performance and efficiency
- Security
- Battery life and optimization
It’s also pushing boundaries with Vision Pro in spatial computing, setting the stage for next-gen interfaces.
4. Rapid Growth in Services
Apple’s services segment—App Store, iCloud, Apple TV+, Music, Pay, Fitness+—has become a high-margin revenue engine. In FY25, services are estimated to cross $100 billion annually.
5. Massive Cash Reserves and Supply Chain Efficiency
With over $160 billion in cash and a global supply chain, Apple has the strength to invest in:
- R&D
- Acquisitions
- Manufacturing diversification (India, Vietnam, etc.)
Competitor Snapshot – 2025 Overview
| Brand | Revenue (2025) | Ecosystem Integration | Services Revenue | Loyalty Score (US) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | $395B+ | Very Strong | $100B+ (est.) | 90%+ |
| Samsung | $240B+ | Moderate | ~$30B | 70–75% |
| $330B+ | Strong (Pixel + Android) | $95B+ | 60–65% | |
| Huawei | $100B+ | Moderate | ~$10B | Limited (Global) |
Figures based on 2024–25 projections and market reports.
Apple’s core strength is its ability to create products people don’t just use—but love, while monetizing those relationships across multiple devices and services.
Weaknesses of Apple
While Apple is admired for its innovation and brand power, it also faces several internal challenges—especially as expectations rise, markets mature, and competitors evolve.
Let’s examine the key weaknesses Apple must address in 2025:
1. Overdependence on iPhone Revenue
Despite growth in services and wearables, Apple still derives over 50% of its revenue from the iPhone. Any slowdown in iPhone sales—due to upgrade fatigue or market saturation—can significantly impact its financials.
2. High Pricing Limits Emerging Market Penetration
Apple’s products often sit at the top of the pricing pyramid, making them inaccessible to large segments of price-sensitive consumers in countries like India, Indonesia, and parts of Africa.
3. Closed Ecosystem Criticism
While Apple’s tightly controlled ecosystem enhances user experience, it:
- Limits flexibility
- Prevents sideloading and app freedom
- Is under scrutiny for anti-competitive practices (especially the App Store fee structure)
4. Slow to Adopt Some Emerging Trends
Apple has been relatively late to market with:
- Foldable phones (Samsung leads here)
- Generative AI integration
- Mixed reality (Vision Pro is first-gen in 2025)
This cautious approach, while deliberate, can cost early-mover advantage.
5. Dependence on Chinese Manufacturing
Although Apple is shifting production to India and Southeast Asia, it still relies heavily on Chinese factories, exposing it to:
- Political tensions
- COVID-style disruptions
- Trade tariffs
In summary, Apple’s biggest challenge is breaking free from its dependence on one product line and ensuring its ecosystem and innovation pace stay competitive across all fronts.
Opportunities for Apple
Apple has the brand trust, financial muscle, and user base to lead the next wave of innovation. In 2025, its greatest opportunities lie in AI, immersive computing, services expansion, and deeper penetration into emerging markets.
Let’s explore the most promising growth avenues:
1. AI & On-Device Intelligence
Apple is gradually rolling out its own generative AI tools, focusing on:
- Private, on-device AI processing
- Smarter Siri and predictive suggestions
- Productivity-focused tools (e.g., writing, summarizing, health insights)
This privacy-first AI approach could differentiate Apple from cloud-based competitors like Google or OpenAI.
2. Vision Pro & Spatial Computing
The launch of Apple Vision Pro marks the company’s entry into mixed reality. With its own operating system (visionOS) and app ecosystem, Apple is set to lead the next era of:
- Spatial computing
- Virtual collaboration
- Immersive content and gaming
3. Services Growth & Health Ecosystem Expansion
Apple continues to expand high-margin services like:
- Apple Fitness+, Health, and Apple Pay Later
- Partnerships with healthcare providers and device-integrated diagnostics
- Enhanced iCloud+ privacy and storage bundles
Recurring revenue from services is forecast to grow 15–20% annually.
4. Emerging Market Penetration (India & LATAM)
With increasing focus on local manufacturing in India, Apple is:
- Opening more Apple Stores
- Offering localized pricing and EMI plans
- Targeting the growing middle class and aspirational segments
India is expected to become Apple’s third-largest market by revenue in the next 2–3 years.
5. Automotive Innovation & Smart Home Expansion
Apple continues to explore:
- Apple Car (still in R&D, possibly as a software-first model)
- Deeper integration with smart home and wearables (Health, HomeKit, CarPlay 2.0)
These verticals could define its next trillion-dollar category.
With a strong focus on user experience, privacy, and premium ecosystems, Apple is well-positioned to lead the convergence of tech, health, and lifestyle in the next decade.
Threats to Apple
Despite its dominance, Apple faces a fast-changing environment where tech disruption, legal pressures, and market saturation could slow growth or erode brand advantages. In 2025, these threats are sharper than ever.
Let’s explore what’s at risk:
1. Global Regulatory Scrutiny
Apple is under increasing fire from regulators in:
- The EU (Digital Markets Act) – forcing sideloading and alternative app stores
- The US – antitrust cases focused on App Store fees and iOS restrictions
- India and South Korea – pushing for payment system flexibility
These could impact App Store revenue, developer relations, and ecosystem control.
2. Stiff Competition from Tech Giants
Apple faces intense competition from:
- Samsung in premium smartphones and foldables
- Google in AI and integrated devices (Pixel, Android, Gemini)
- Microsoft in productivity tools, AR, and cloud platforms
- Chinese OEMs (e.g., Xiaomi, Oppo, Huawei) in pricing and innovation
These brands are closing gaps in design, performance, and user experience.
3. Supply Chain Dependence & Geopolitical Risks
Apple’s hardware supply is still heavily tied to:
- Chinese factories and vendors
- Taiwan-based chip foundries (TSMC)
Any disruption due to politics, war, or trade barriers could cripple production timelines.
4. Saturation of Core Product Markets
Most of Apple’s user base now owns:
- A recent iPhone
- Mac or iPad
- Watch or AirPods
This results in longer upgrade cycles and limited scope for hardware-based revenue growth—unless new categories emerge quickly (e.g., Vision Pro or Apple Car).
5. Privacy Backlash or Brand Fatigue
While Apple positions itself as a privacy leader, it must balance:
- Monetization of services
- Data personalization
- Avoiding overreach like ad tracking or subscription bundling fatigue
A misstep could damage trust, especially among Gen Z and younger users.
To maintain its edge, Apple must defend its walled garden carefully, diversify revenue faster, and keep innovating—without losing its premium, privacy-first identity.
Strategic Insights & Key Takeaways
Apple’s dominance in 2025 is not by accident—it’s the result of decades of user-focused design, ecosystem control, and premium branding. But as the tech landscape evolves, so must Apple’s strategy.
Here’s what the SWOT analysis reveals:
- Strengths like device integration, loyal user base, and chip innovation keep Apple ahead in product experience.
- Weaknesses such as iPhone dependency and closed ecosystem risks could hinder diversification.
- Opportunities in AI, mixed reality, services, and healthcare could define Apple’s next $1 trillion growth wave.
- Threats from regulators, competitors, and global supply tensions require greater agility and regional diversification.
To succeed in the future, Apple must remain what it has always been: bold in innovation, obsessed with experience, and relentless about privacy and design perfection.
Conclusion
Apple’s story is one of vision, reinvention, and seamless control over its ecosystem. From the iPod revolution to the iPhone era, and now to Vision Pro and AI-first platforms—Apple continues to define how humans interact with technology.
But 2025 brings new pressures: global scrutiny, slowing hardware growth, fierce competition, and evolving consumer expectations.
To lead the next decade, Apple must shift from being hardware-first to experience-first—combining privacy-respecting AI, health-centric features, and spatial interfaces into a lifestyle that feels intelligent, intuitive, and irreplaceable.
With the right bets, Apple could very well shape the next computing era, just as it did the last one.
❓ FAQs – SWOT Analysis of Apple
1. What is Apple’s biggest strength in 2025?
Apple’s biggest strength lies in its ecosystem lock-in—offering seamless integration across devices, services, and platforms with unmatched user loyalty.
2. How is Apple competing in AI and mixed reality?
Apple is rolling out on-device AI tools for Siri, health, and productivity, and leading spatial computing with its Vision Pro headset launched in early 2024.
3. Is Apple still dependent on iPhone sales?
Yes. Despite services and wearables growth, the iPhone still contributes over 50% of Apple’s total revenue, making diversification a strategic priority.
4. What risks does Apple face in 2025?
Key threats include regulatory pressure on App Store practices, global supply chain risks, competitive innovation from Google and Samsung, and slowing iPhone upgrade cycles.
5. Is Apple expanding in emerging markets?
Yes. Apple is aggressively investing in India and Southeast Asia with local manufacturing, exclusive stores, and region-specific pricing to grow its global market share.
Explore more